There is a pressing need for methods delivering therapeutic macromolecules to their intracellular targets at low nanomolar concentrations without endosomal entrapment. Certain viruses and bacterial toxins exploit lipid raft-mediated endocytosis to deliver macromolecules in their functional form without degradation, which we set out to mimic in our approach. These proteins of viral and bacterial origins trigger the desired intracellular delivery by binding to gangliosides at the lipid raft entry points.
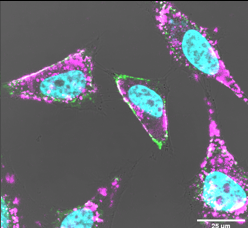
We discovered a pentapeptide sequence that specifically captures the lipid raft marker ganglioside GM1. Thus, it triggers endocytosis on various human live cell lines. The cargo-loaded endosomes show limited fusion with lysosomes. Several immunoglobulin G complexes were successfully delivered into live cells at extracellular concentrations ranging from 20 to 160 nM. The antibodies’ molecular recognition regions remained functional, and the escape of the functional cargo protein to the cytosol was observed without any additional endosomal escape sequence. The carrier tag was not toxic even in the high micromolar region.


The patent for the tag-triggered cytosolic delivery of macromolecules has been filed. The IP protection process is in progress with the EU and US patent offices. We are continuously developing other coupled patent applications to further secure our technology, ensuring well-protected investment.